Neuro Balance
Neurotransmitter Support*
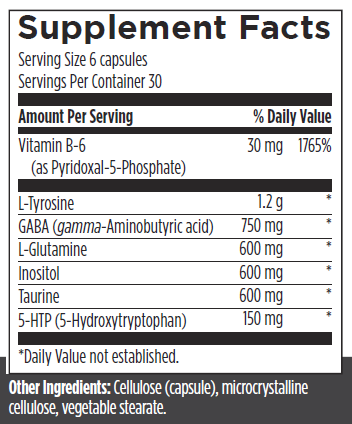
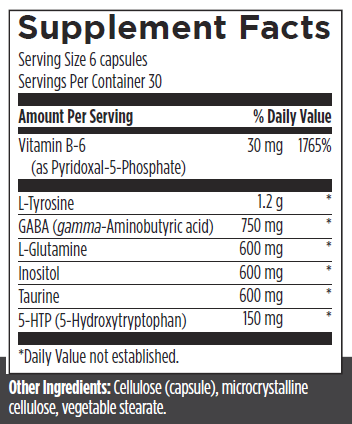
Neuro Balance is a targeted blend of amino acids and other building blocks to support mental focus, neurotransmitter balance, and a healthy mood. It contains clinically relevant amounts of gamma‑aminobutyric acid (GABA) to help support mental focus and mood health.* It also provides L‑glutamine and L‑tyrosine, building blocks for GABA and dopamine, to help support neurotransmitter balance, a healthy mood, and a normal stress response.*
This formula contains 5‑hydroxytryptophan (5‑HTP), a building block to the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin.* Serotonin is essential for brain functioning, gastrointestinal motility, and mood health. Melatonin helps support sleep quality and duration.*
Neuro Balance also features the bioactive form of vitamin B6 as pyridoxal 5‑phosphate (P5P), which is an essential molecule for the production of serotonin and conversion to melatonin.
VIEW SPEC SHEET



Explore detailed product information, including technical sheets or official certificates of analysis.